IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
What you need to know about IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
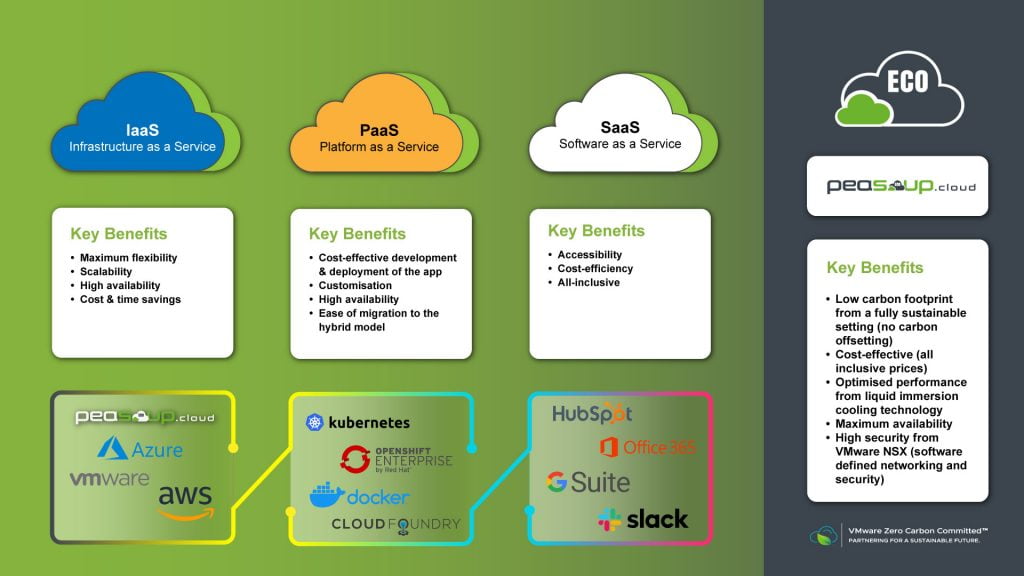
The adoption of a cloud environment in the business world has been on the rise. They are moving away from traditional on-premise IT solutions. They are now relying more on infrastructures, software, and platforms that are offered as a service. If you are considering moving your business to the cloud, you need to be aware of the available types of cloud computing terms, namely: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). These are three ways that describe how the cloud can be used in a business. A significant number of businesses that have adopted cloud base solutions use SaaS and IaaS, service models. Others have sought the services of developers to create applications using PaaS.
SaaS (software as a service)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software licensing and delivery model where cloud solutions users access software online through a subscription rather than buying and installing it in their systems. With this model, data can be accessed from any device as long as you have an internet connection and a web browser. It involves software that is available through a third party over the web. Some of the popular SaaS providers are Dropbox, Slack, Big Commerce, ZenDesk, and Hubspot among others. With SaaS, you do not need to download and install applications. Even when it comes to technical issues the vendor leads to streamlined support and maintenance for your business. With this cloud delivery model, the time needed for installing, managing, and upgrading software is greatly reduced. This frees your business the time that the technical staff would spend to ensure the system works. Instead, they have plenty of time to work on other pressing matters and issues.
Some of the distinguishing characteristics include:
- Management from the central location
- Hosting on a remote server
- The vendor is responsible for updates and maintenance
A business that needs to launch quickly and affordably will find SaaS beneficial. Some of the main concerns with SaaS include:
- interoperability issues where integration with the existing system
- Vendor lock-in where users may join easily but find it hard to leave
- With deep and complex integrations that are required, there can be limitations on how SaaS service can be used
- Lack of control
- Downtime
PaaS (platform as a service)
Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) is a full development and deployment model. It has resources that allow delivery through the internet of simple or complex cloud tools on a use-basis. It includes infrastructure such as servers, storage, development tools, database management systems, and networking among others. It is designed to support the full web application cycle, from building, testing, deployment, management, and maintenance. With this model delivery, your business avoids the expense and complexity of acquiring and management of software licenses as well as the underlying infrastructure. Its delivery model is similar to Saas only that it provides a platform for the creation of software. With such a delivery model, you do not have to worry about operating systems, storage, or updates. You have the freedom to concentrate on building the software.
Using PaaS comes with the following benefits:
- It provides a simple and cost-effective development and deployment of the app
- Scalability
- Highly available
- Ease of migration to the hybrid model
Its limitations include concerns with data security, complexity in integration, vendor lock-in, and loss of operational control which may affect how the model is managed, provisioned, and operated.
IaaS (infrastructure as a service)
IaaS is a cloud model that delivers IT infrastructure such as computing, network, and storage resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. With IaaS, you lease or rent the computing resources that you need. It saves your business from acquiring components that you may not need at a particular time. It is scalable and at the same time offers your business greater flexibility when compared to on-premises solutions. The on-demand model allows you to get what you need and when you grow can adjust the delivery of resources. Apart from being highly flexible, and scalable, the delivery model puts the control over the IT infrastructure back into your hands. Some of the limitations that come with this model include:
- Need to upgrade or replace legacy systems
- Security
- Additional training may be needed.
IaaS provides users with maximum flexibility and a general data centre. PaaS is built over an IaaS system to minimize the need for administration and also allows full focus on development as opposed to infrastructure management. SaaS provides users with unique ready-to-use solutions which meet their business needs. The increasing popularity of these cloud-based models has greatly reduced the need for on-premise hosting. Users have more options and flexibility.